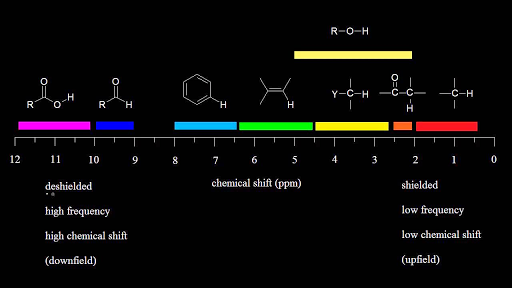
Table of characteristic proton nmr shifts type of proton type of compound chemical shift range ppm rch 3 1 aliphatic 0 9 r 2 ch 2 2 aliphatic 1 3 r 3 ch 3 aliphatic 1 5 c c h vinylic 4 6 5 9 c c h vinylic conjugated 5 5 7 5 c c h acetylenic 2 3 ar h aromatic 6 8 5 ar c h benzylic 2 2 3 c c ch 3 allylic 1 7 hc f.
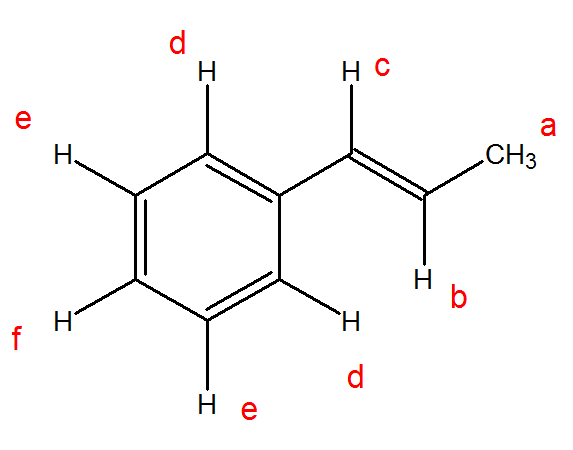
Vinylic proton nmr shift.
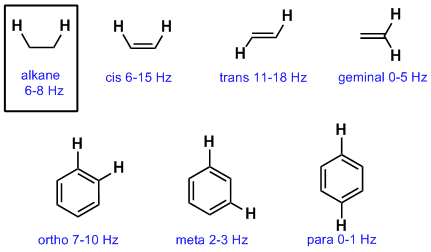
Assigning the 1h nmr signals of aromatic ring 1h atoms assigning 1h nmr signals of 1h atoms on an aromatic ring based upon their chemical shift and coupling can be accomplished in a number of different ways which will be detailed below.
Notice that the proton closest to the carbonyl group is at a higher chemical shift than the proton in cyclohexene 6 05 ppm for cyclohexenone vs.
0 8 1 5 ppm alkane c h.
Meo2c ch c nme2 co2me has a chemical shift of 4 49 for the vinylic proton in cdcl3.
The greater the substitution on the carbon bearing the hydrogen the further downfield higher frequency the resonance occurs.
Table of characteristic proton nmr chemical shifts.
Typical h nmr shift ranges.
We know that a proton alpha to a carbonyl group is pulled downfield.
Type of proton type of compound chemical shift range ppm rc h 3 1 aliphatic 0 9 r 2 c h 2 2 aliphatic 1 3 r 3 c h 3 aliphatic 1 5 c c h vinylic 4 6 5 9 c c h vinylic conjugated 5 5 7 5 c.
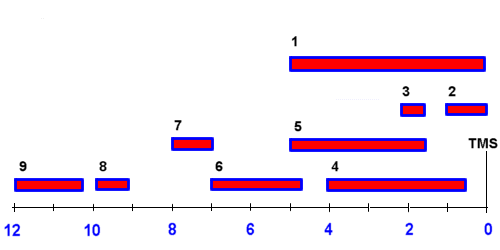
Tetramethylsilan tms ch 3 4 si is generally used for standard to determine chemical shift of compounds.
C h acetylenic 2 3 ar h aromatic 6 8 5 ar c h benzylic 2 2 3 c c c h.
This is a general trend add approximately 0 2 0 4 ppm for each additional alkyl group.
These methods which range from very simple to somewhat sophisticated are complimentary to one.
Chemical shift d type of proton examples chemical shift in ppm comments.
A summary table of chemical shift information is given in appendix iii.
Nmr spectra of alkenes two characteristic proton nmr absorptions for alkenes are the absorptions for the protons on the double bond called vinylic protons red in the following structures and the protons on.
In other words frequencies for chemicals are measured for a 1 h or 13 c nucleus of a sample from the 1 h or 13 c resonance of tms.
Nmr chemical shift values table in the previous post we talked about the principles behind the chemical shift addressing questions like how the ppm values are calculated why they are independent of the magnetic field strength and what is the benefit of using a more powerful instrument.
1 h nmr chemical shifts.
30 c using 1h and 31p nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Characteristic proton chemical shiftstype of protonstructurechemical shift ppmcyclopropanec3h60 2primaryr ch30 9secondaryr2 ch21 3tertiaryr3 c h1 5vinylicc c h4 6 5 9acetylenictriple.
Come anywhere in the proton nmr spectrum.